

| PROJECTⅠ 担当 |



|
|---|
| PROJECTⅠ 担当 |



|
|---|
Project 1 aims to develop the reaction process which realizes the manufacturing of calcium carbonate concrete (CCC). The University of Tokyo, Taiheiyo Cement Corporation and Tokyo University of Science are in charges of this project. As explained in the general outline, in order to efficiently use the extracted calcium (Ca), Ca is reacted with carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere to form calcium carbonate. At the same time, calcium carbonate bounds crushed concrete (recycled aggregate) each other to compose hardened material.

Calcium carbonate concretion occurring in nature, some particles such as sand present inside the calcium carbonate shell and form the hardened material. If this natural process can artificially imitate, our challenging CCC comes into real.

Aggregate is prepared from crushing demolished concrete.
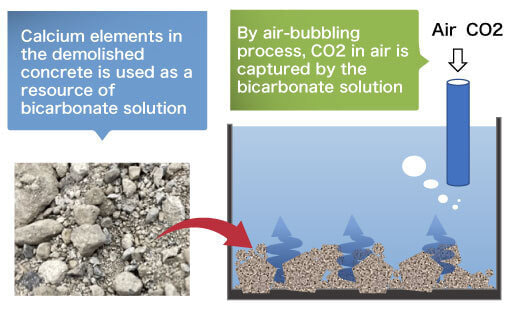
In contrast, since there is abundant Ca in concrete, calcium bicarbonate solution is prepared from aggregate immersion and air introduction into water.

The solution passes between aggregates with heating, then calcium carbonate precipitates from the solution. This reaction enables to produce CCC
Currently, we are improving the manufacturing process in order to increase the size of the specimens, increase the strength, and produce large quantities.


| PROJECTⅡ 担当 |


|
|---|
| PROJECTⅡ 担当 |


|
|---|
Project 2 is a project to manufacture raw materials for making calcium carbonate concrete (CCC). The members from Hokkaido University and Masuo Recycle Inc. contributes to this project.
The raw material for CCC is the "crushed concrete" obtained when the concrete structure is dismantled. This crushed material is generally called "recycled roadbed material" in Japan, and often used as a roadbed material in road construction. However, it has not yet been fully utilized with an awareness of immobilizing CO2 on recycled roadbed materials.

Therefore, Project 2 is developing technology to increase the value of this recycled roadbed material as a raw material for CCC. In order for the reaction process of Project 1 to proceed effectively, the particle size of the crushed concrete obtained from the demolished concrete structure is adjusted, and as much CO2 as possible is fixed into the cement paste adhering to the surface, and it is converted to calcium carbonate. The main mission is to develop technology to make it.

At Projetct2, we are developing a manufacturing method for raw material of CCC with the aim of fixing CO2 from the atmosphere (Direct Air Capture) using common and simple control methods such as ventilation, agitation, and temperature / humidity control.

We have set up a scalable lab plant on the premises of Masuo Recycle Inc. where we can crush concrete wastes, adjust the particle size, and carbonate it for conducting actual operation experiments. We are also developing technology to accelerate carbonation using small equipment at the laboratory level for applying to the scalable plant in Hokkaido Univeristy.


| PROJECTⅢ 担当 |




|
|---|
| PROJECTⅢ 担当 |




|
|---|
In Project 3, the following research and development is being carried out toward the social implementation of calcium carbonate concrete (CCC), comparing with the case of conventional concrete.
- Examination of structural type, structural design method, durability design method, member manufacturing method and construction method which are suitable for CCC structures
- Formulation of an optimal supply chain for CCC
- Evaluation of CO2 emissions and captures throughout the life cycle of CCC structures
- Examination of the contents of laws and standards and the method of their enactment and revision necessary for realizing the social implementation of CCC
1 Examination of structural type, structural design method, durability design method, member manufacturing method and construction method which are suitable for CCC structures
Based on the special features and performance of CCC, examinations are made on the adaptation of precasting, prestressing, CFT (concrete filled tube), etc., and on the applicability of structural design method and durability design method for conventional reinforced concrete structures to CCC.
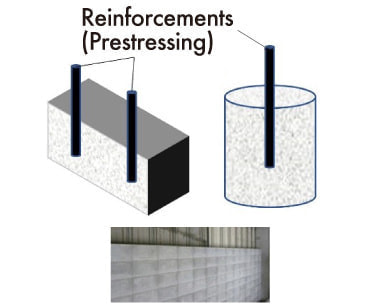
(1)Block structure
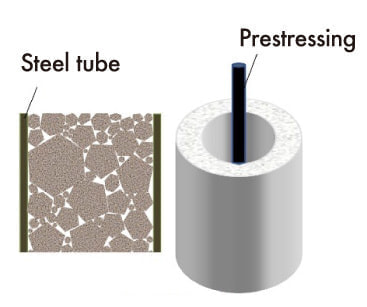
(2) Frame structure
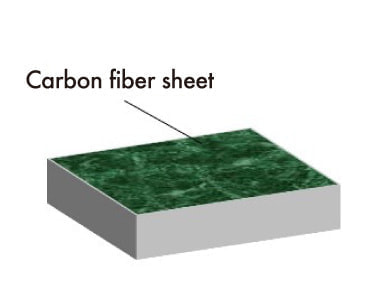
(3) Wall structure
2) Formulation of an optimal supply chain for CCC
After predicting the future’s amount of demolition and new construction for each type of concrete structure based on regional characteristics, examinations are made on the optimum installation location and the optimum scale of CCC material production facilities and CCC member manufacturing facilities.
Estimation of the manufacturable amount of CCC raw materials
Survey of various statistical data on new construction, stock, demolition, etc. of buildings
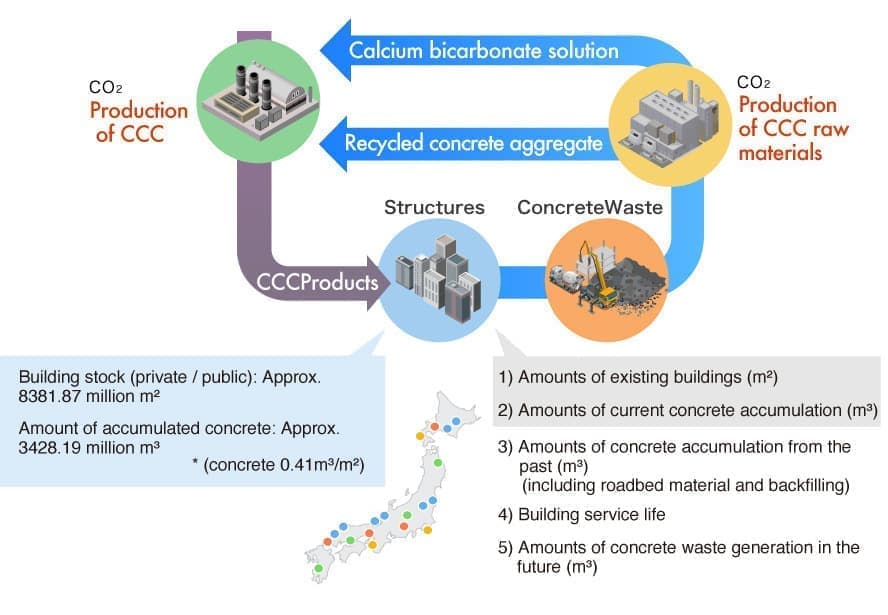
Examination of location of intermediate processing facilities, CCC raw material manufacturing factories, CCC manufacturing factories suitable for C4S
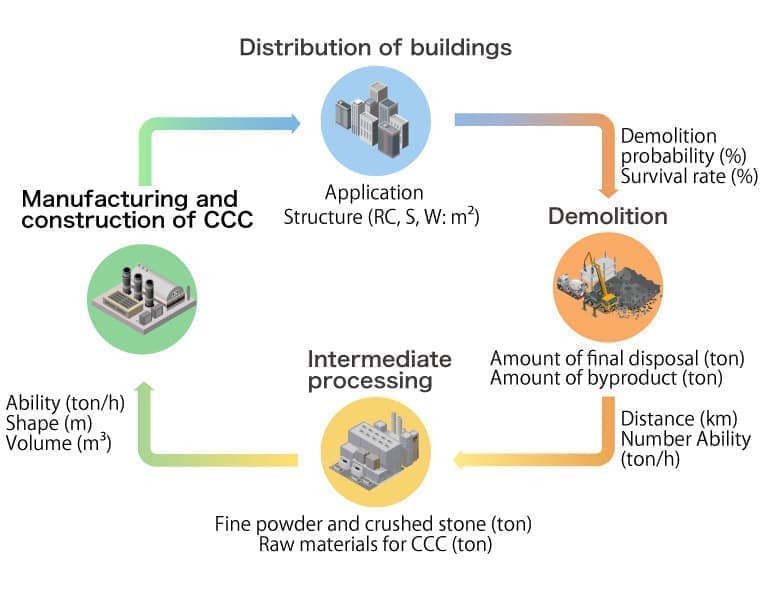
3) Evaluation of CO2 emissions and captures throughout the life cycle of CCC structures
While investigations are made on CO2 emissions at intermediate treatment facilities for concrete waste and manufacturing plants for precast members for conventional concrete structures, and predictions are made on CO2 emissions during the production of CCC materials and the production of CCC members. Consequently, the superiority of C4S is clarified.
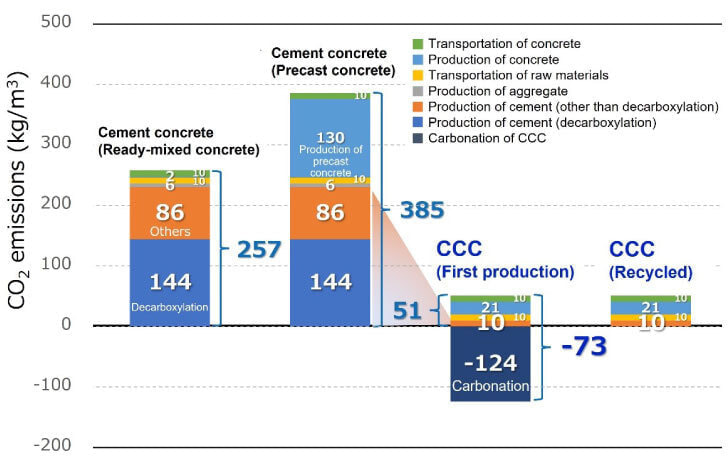
4) Examination of the contents of laws and standards and the method of their enactment and revision necessary for realizing the social implementation of CCC
Examinations are made on the procedure for realizing CCC buildings in accordance with the current Building Standard Law of Japan and the revising procedure and revised contents of the Building Standard Law of Japan after the establishment of Japanese Industrial Standards.
| Year |
Development and dissemination |
CCC products | Establishment & revision of laws and standards |
| 2023 | Achieving compressive strength of 12MPa | 0 ton |
|
| 2025 | Construction of mock up structure |
100 ton | |
| 2030 | Construction of several low-rise CCC buildings |
2,000 ton |
1. Obtaining ministerial approval based on Article 20 of the Building Standard Law |
| 2040 | 1.725 times increase every year | 345,000 ton | 2. Establishment of Model Codes and Standards of Architectural Institute of Japan 3. Amendment of Ministry of Construction Notification No. 1446 (Technical Standards) 4. Obtaining ministerial approval based on Article 37, Paragraph 2 of the Building Standard Law 5. Establishment of Japanese Industrial Standard 6. Amendment of Ministry of Construction Notification No. 1446 (Technical Standards) 7. Compliance with Article 37, Paragraph 1 of the Building Standard Law |
| 2050 | 50% of concrete structures made of CCC |
110,000,000 ton |

